The term “blockchain” has been on everybody’s lips for quite some time, but only a few know what it means and how it functions. As this technology becomes popular and widely used, you must equip yourself with the knowledge so that you use it to advance your career and not miss out on what it has to offer in the future.
This is why we have put this article together to educate you on the topic and help you understand how to use blockchain transactions for different activities, like playing games at an online casino, exchanging, and so on. We will explain blockchain technology, what it does, how it works, and the types of blockchains that operate in the digital space.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a data storage warehouse for storing data. Any information stored here is safe and challenging to be altered by intruders or hackers.
A blockchain is a distributed ledger(DLT) that allows record-keeping across many networks of computers known simply as “nodes.” These nodes are responsible for verifying, authorizing, and storing data within the blockchain.
How the Technology Works
Blockchain technology stores public transactional information, often known as blocks or chains, across multiple databases linked by peer-to-peer nodes. This is commonly referred to as a digital ledger.
Every transaction in this ledger is approved by the owner’s digital signature, which verifies the transaction and protects it from fraud. The data on the digital ledger is, therefore, safe.
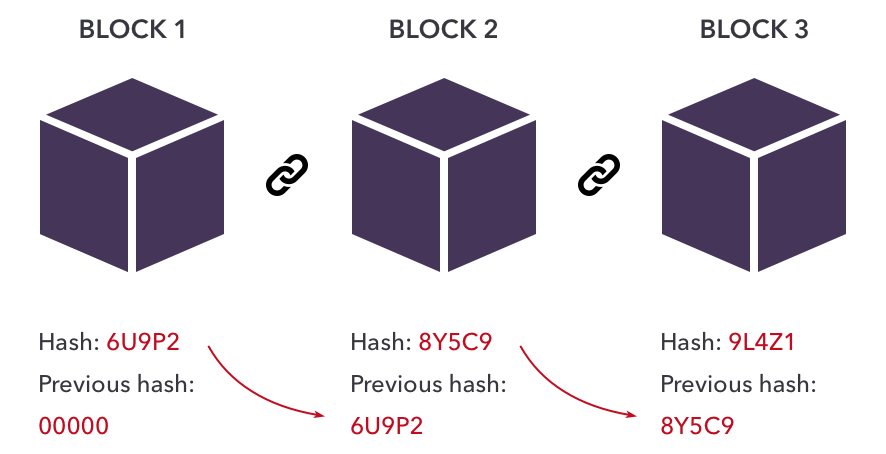
The technology organizes data symmetrically added to the ledger into blocks. Each block consists of a certain amount of data, and new blocks are constantly added to this ledger forming a chain of ledgers.
Every block has its unique identifier known as “hash.” The hash protects the data within the block from hackers. Once data is added to the ledger and encrypted within a hash, it immediately records and becomes unchangeable.
For a transaction to get stored in the blockchain, it must follow some due process like authentication and be duly authorized. Let’s briefly discuss these two processes:
Authentication
Blockchain was initially designed to operate without a central authority or regulations from banks or the government. However, transactions on the technology still have to be monitored and authenticated to avoid discrepancies.
This authentication is done by employing the use of cryptographic keys. This is a string of data just like your typical phone password to identify users and provide access to their wallets or accounts in the system.
Every user is given a private key which is only known to the user, and a public key that everyone can see. Using private and public keys creates a secure digital identity to authenticate a user via their digital signatures and to make transactions.
Authorization
Every transaction on the blockchain technology needs to be authorized and verified for it to be added to the block.
For instance, in a public blockchain, the decision to add a transaction to the chain has to be agreed on by all the parties involved. All “nodes” must approve and verify the transaction’s validity.
Types of Blockchain
There are four types of blockchains, and we will discuss them below:
Private blockchain network: This type of blockchain operates on a closed network. Private organizations use it to customize their authorization and accessibility preferences.
Public blockchain network: This is the most common type of blockchain used by bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies to solve security flaws and centralization issues.
Permission blockchain network: This is sometimes referred to as a hybrid blockchain. It is mainly used by organizations looking to enjoy the best freedom or accessibility of private and public blockchain networks.
Consortium Blockchains: This type of blockchain is also built on the components of private and public blockchains and offers adequate security to organizations that use it.
Proof of Work and Proof of Stake
Proof of Work involves solving complex mathematical problems to add a block to the chain. The act of unraveling this mathematical problem is known as mining. These miners are rewarded with cryptocurrencies, but mining is quite tricky as the odds of solving the mathematical problem are about one in five trillion.
The process requires considerable computing power, which uses large amounts of energy. On the other hand, Proof of Stake is the validation consensus protocol, where each person must have a stake in the blockchain.
This is usually possible when a person owns some cryptocurrency before being given a chance to select, verify and validate transactions. Proof of Stake saves considerable resources and human resources required for mining.
Blockchain technologies have significantly evolved as “Smart Contracts” are now used instead, automatically executing transactions when all the participants have fulfilled specific conditions.