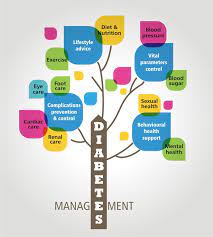
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterised by high blood glucose levels resulting from the body’s inability to produce or use insulin effectively. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates blood glucose levels in the body. When insulin production is inadequate, or the body cannot use insulin effectively, blood glucose levels rise, leading to diabetes.
Managing Diabetes for a Healthy Life

Efficient management of diabetes is an imperative endeavour to preclude or curtail the hazard of associated complications. These complications are not confined to a single region of the anatomy, but rather can encompass the eyes, kidneys, nerves, and cardiovascular system. Hyperglycaemia can impede the optimal function of blood vessels and nerves, thereby instigating a plethora of complications including neuropathy, nephropathy, and retinopathy. Notably, diabetes is also an eminent perilous antecedent to cardiovascular disorders.
Prevention of Complications
For preventing the complications of Diabetes, Diabetes Tests prove to be among the best. We highly recommend you get Diabetes Tests frequently.
The avoidance of complications necessitates the regulation of glycaemic levels, consumption of wholesome sustenance, participation in habitual exercise, and preservation of a salubrious mass. It is imperative to keep glycaemic levels within a specific ambit, requiring constant monitoring and maintenance.
This endeavour can be achieved through a symbiotic approach of pharmaceutical intervention, ingestion of healthy edibles, and physical activity with recurrent regularity. The consumption of a healthy diet can aid in the control of blood glucose levels, ameliorating the chance of developing complications. In addition, habitual physical activity is instrumental in reducing glycaemic levels and improving insulin sensitivity.
The management of weight constitutes an indispensable aspect of both prevention and management of diabetes. A surplus of fatness and obesity increases the likelihood of developing diabetes and amplifies the risk of regulating glucose levels in the bloodstream. By integrating wholesome eating habits with physical activity on a regular basis, a healthy weight can be attained.
In addition, it is paramount to conduct regular surveillance of blood pressure and cholesterol levels in order to prevent and manage diabetes. Both elevated blood pressure and hypercholesterolemia function as precursors for cardiovascular diseases that emerge as the foremost reason for mortality in people afflicted with diabetes. Mitigation of blood pressure and cholesterol levels may be attained through either medicinal treatment or modifications in lifestyle.
Complications
Despite the meticulous efforts to avert complexities, a subset of diabetic patients may still be susceptible to developing complications. It is imperative to manage blood glucose levels in order to prevent and control complications. Prolonged periods of elevated blood glucose levels can inflict severe harm to blood vessels and nerves. By managing blood glucose levels effectively, the onset and progression of these complexities can be slowed down or even prevented.
In the unfortunate event of complications showing, a combination of medication, lifestyle alterations, and medical interventions may be employed as part of the management plan. For instance, physicians may opt to prescribe medications to curtail blood pressure or cholesterol levels. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as smoking cessation and weight reduction may be proposed as plausible interventions. In rare instances, medical interventions such as surgery or dialysis may become necessary to manage the complications effectively.
Diabetes Management Strategies
Managing diabetes effectively requires the utilisation of a diverse range of tactics, encompassing diabetes self-management education and support, medication, and technology. With the aid of diabetes self-management education and support, individuals with diabetes can acquire knowledge and techniques to manage their condition in an optimal manner.
Such education may encompass teachings on prudent dietary habits, physical activity, blood glucose monitoring, and medication management. Furthermore, the provision of support from healthcare professionals and peers can be an efficacious method for managing stress and anxiety related to diabetes.
Medication plays a vital role in the management of diabetes for numerous individuals. The range of medications may encompass insulin, oral medications, or injectables. Oral medications may encompass metformin, sulfonylureas, or DPP-4 inhibitors. Additionally, injectable medications such as GLP-1 receptor agonists or SGLT2 inhibitors may be prescribed as a viable treatment option.
The nascent field of technological innovation has yielded wondrous solutions to the age-old problem of diabetes management. Amongst these novel tools are Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) devices, which offer instantaneous and accurate feedback on blood glucose levels. This real-time information facilitates more meticulous medication dosages and lifestyle changes, elevating the level of precision in diabetes management to unprecedented heights. Insulin pumps, too, offer a promising solution, delivering the essential hormone in a steady stream throughout the day, and mitigating the need for multiple injections. The conjunction of these technological advancements serves as a beacon of hope for those grappling with the intricacies of diabetes management, heralding a new era of precision and ease.
Coping with Diabetes

The management of diabetes is a difficult and demanding undertaking. Diabetes, being a chronic medical condition, necessitates an unwavering dedication to maintaining blood glucose levels within a healthy range, regularly consuming prescribed medications, and adapting one’s lifestyle accordingly. In addition to the physical implications of diabetes, the psychological consequences of this condition are equally consequential. Coping with the emotional turbulence of diabetes is therefore an indispensable component of managing this disease.
The emotional response of an individual to diabetes can differ dramatically. Some individuals may find themselves inundated and besieged by the exigencies and obligations associated with diabetes management, while others may be beset with a confluence of anxiety and depression, brought on by their diabetic condition.
As a result, experiencing a range of emotions is an ordinary and understandable response to grappling with diabetes, and availing oneself of appropriate assistance and guidance can prove to be a valuable and efficacious means of dealing with these emotions.
One of the most efficacious coping methodologies for managing stress and anxiety related to diabetes is to remain apprised of the condition. Assimilating as much information as practicable regarding diabetes, its aetiology, symptoms, and therapeutic alternatives, can serve to confer a sense of autonomy over one’s condition. This, in turn, can also inculcate a deeper comprehension of the criticality of self-care and adopting a proactive stance towards managing diabetes.
Another efficacious coping strategy for managing diabetes-related stress and anxiety is to cultivate a robust support system. This may encompass family members, acquaintances, healthcare providers, or support groups.
Physical exercise and activity can also function as effective coping strategies for managing diabetes-related stress and anxiety. Consistent physical exercise can aid in blood sugar regulation, ameliorate overall health, and mitigate stress. Exercise can additionally serve as a healthy conduit for releasing emotions and enhancing mental well-being.
Conclusion
Effective management of diabetes is crucial for preventing or reducing the risk of complications. Prevention of complications involves managing blood sugar levels, eating a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Control of complications involves a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and medical interventions. Diabetes management strategies include diabetes self-management education and support, diabetes medications, and the use of technology for diabetes management.
Coping with diabetes involves practising mindfulness, seeking support from friends and family, and connecting with other people with diabetes through support groups or online communities. Regular diabetes tests are essential for early detection and effective management of diabetes. Taking proactive steps towards diabetes management can lead to a healthy and fulfilling life.
Do you think you might be at risk of Diabetes? Book a Diabetes Blood Test immediately with PathKind Labs!